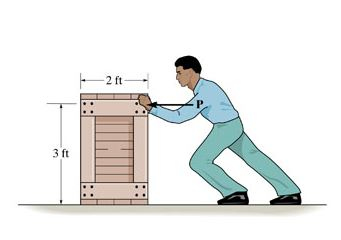
One worker pushes forward on the crate with a force of 270 n while the other pulls in the same direction with a force of 130 n using a rope connected to the crate.
A 100 kg crate sliding on the floor.
A f m 25n 100kg 0 25 m s 2.
The coefficient of static friction is 0 4.
One worker pushes forward on the crate with a force of 380 n while the other worker pull in the same direction with a force of 350 n using a rope.
What is the crate s coefficient of kinetic friction on the floor.
A horizontal force latex overset to p latex is applied to the crate.
Both forces are horizontal and the crate slides with a constant speed.
Both forces are horizontal and the crate slides at a constant speed.
Here s how to crack it the normal force on the object balances its weight so f n mg 100 kg 10 m s 2 1 000 n therefore f static friction max f f static max µ s f n 0 4 1 000 n 400 n.
A 100 kg crate sliding on a floor is brought to a stop by 25 n force.
This is the maximum force that.
The coefficient of static friction between the crate and floor is 0 700 and the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0 600.
What is the deceleration of the crate.
Two workers are sliding a 100 kg crate across the floor.
P m v 80kg x 2 5 m s 200 kg m s.
A 100 kg crate sliding on the floor is brought to a stop by a 25 n force.
After t 0 second it acquires pure rolling motion as shown in figure.
A uniform disc of mass and radius r is projected horizontally with velocity v c on a rough horizontal floor so that it starts off with a pure sliding motion at t 0.
μ is the coefficeient of friction.
Calculate the velocity of the centre of mass of the disc at t 0.
If a force of 250 n parallel to the floor is applied to this mass the magnitude of the force of static friction on the crate is 250 n.
If a force of 250 n parallel to the floor is applied to the crate what s the magnitude of the force of static friction on the crate.
A 20 0 kg crate is at rest on a floor as shown in.
Two workers are sliding a 300 kg crate across the floor.